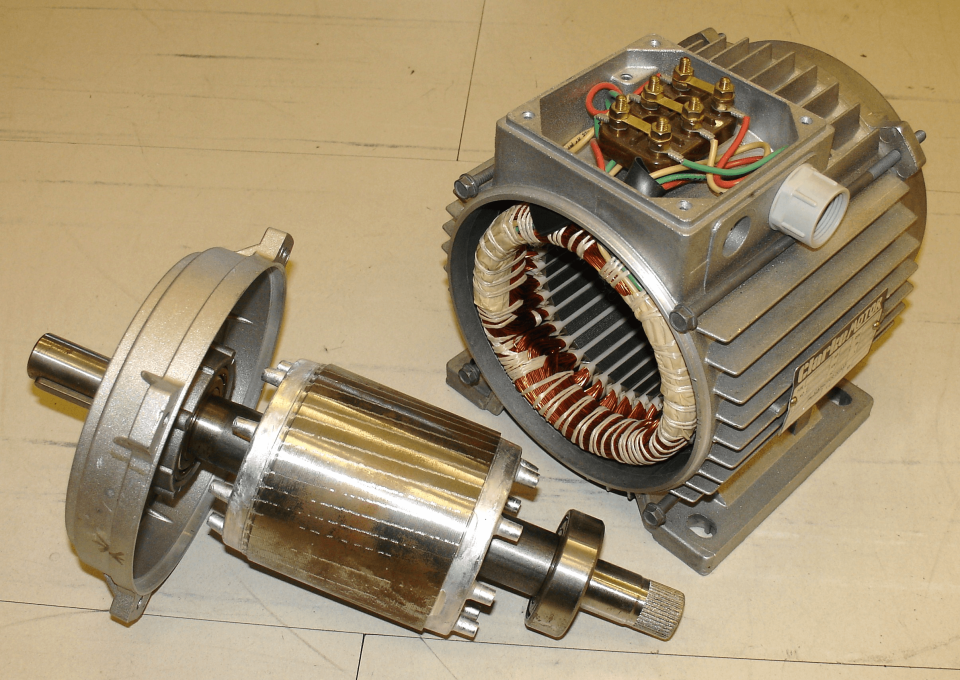
Electric motor winding machines form the foundation of the motor production industry, ensuring that motors operate capably and reliably. These machines are responsible for winding the coils that are necessary for the motor’s function. While the concept might seem simple, designing an efficient electrical motor winding structure involves miscellaneous key considerations.
Let us delve into these design applications of electric motor winding machines and understand their importance.
The Importance of Material Selection
Selecting the right materials is important when designing electrical motor winding machines. The materials used must withstand operational stress, be economical, and backing the intended efficiency of the motor.
1. Core Materials
Core materials decide the efficiency and acting of the winding machine. Silicon steel is often the best choice for its excellent magnetic features and skill to minimize energy deficit. However, in certain uses where weight is a concern, designers might choose substitutes like amorphous steel or new specialized alloys.
2. Wire and Insulation
The choice of wire and its padding is another integral design aspect. Copper is commonly the go-to wire material due to allure superior conductivity. However, aluminum maybe a viable alternate when cost savings are prioritized. The insulation must be selected depended on the machine’s functioning temperature and voltage necessities, with alternatives ranging from enamel coatings to more progressive polymer films.
3. Precision and Control
An electrical motor winding machine must offer accuracy and control to ensure the logical performance and longevity of the motors it produces. This accuracy stems from both mechanical and software elements.
4. Mechanical Precision
The machinelike setup of the winding gadget, containing the spindle and tensioning systems, must be designed to assert precise control over the wire all along the winding process. This control is essential for lowering wire damage and guaranteeing uniform coil density, that precisely impacts motor efficiency.
5. Software Integration
Modern winding machines handle sophisticated software for precise control. This software furthers automated winding processes, reinforcing accuracy and adeptness. The integration of sensors and feedback schemes allows real-time adjustments throughout operations, further optimizing the winding method.
6. Ergonomics and Usability
While the technical aspects of winding machinery are critical, the design must also acknowledge ergonomics and usability. An instinctive design minimizes operator tiredness and error, improving overall productivity.
7. User Interface
The user interface should be instinctive, providing controllers with smooth access to controls and machine backgrounds. Touchscreens with clear graphical displays are becoming more and more common, allowing operators to adjust criteria quickly and capably.
8. Maintenance and Accessibility
Designs should facilitate smooth maintenance and troubleshooting. Quick access to key elements can considerably reduce spare time, making it smooth for technicians to perform routine sustenance and address any issues that arise.
9. Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency is an increasing concern in the design of winding machines. With manufacturers aiming to lower functional costs and environmental impact, machines must be designed to reduce energy consumption.
Conclusion
While these considerations may not be essential for all, they specify priceless visions for those involved in the motor production enterprise, paving the habit for modernizations that meet the demands of modern uses.